Phthalic anhydride is a key chemical intermediate in applications from phthalate plasticisers to polyesters. Many types of polyesters can be made via reaction with glycols, from alkyd resins and unsaturated polyester resins to polyols for polyurethanes (PU).
Tecnon OrbiChem’s data platform OrbiChem360 calculates global production capacity at 6.4 million metric tons in 2022 – over half in China or Northeast Asia, and all coming from petrochemical-based sources. Since there are currently no commercial biobased phthalic anhydride (PA) products available, a non-fossil aromatic could prove a gamechanger.
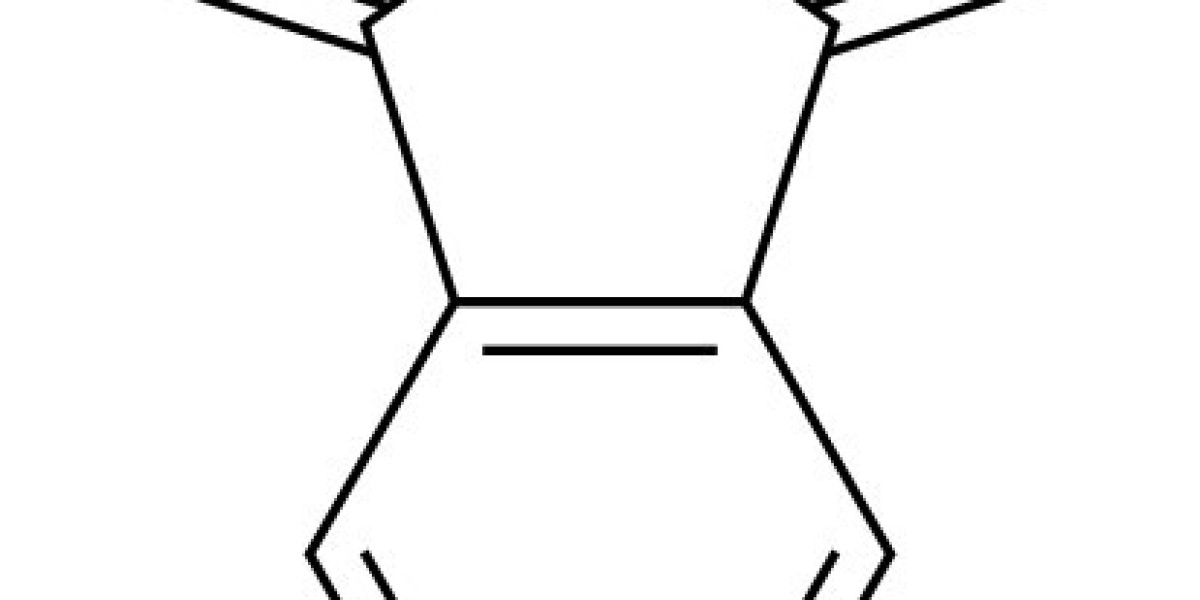
Renewable chemistry startup Relement claims to have uncovered the missing link needed to create a largely sustainable alkyd/polyester coatings. Noting that the aromatic is the key ingredient needed to make coatings sustainable, Relement chemists set out to replace that petrochemical element with a bio-derived alternative that gives coatings the gloss, scratch resistance and UV-stability of traditionally-made coatings.
Not only does Relement’s bio-MPA (3-methyl phthalic anhydride) replace the fossil ingredient PA in coatings, the Dutch startup says its product increases coatings hardness – making it potentially longer-lasting than its petrochemical counterpart. After demonstrating the product’s viability at lab level, Relement enlisted the R&D arm of science company Solvay to scale-up its proprietary product in April 2022.
The starting material for Relement’s biobased aromatic MPA is 2-methylfuran (2MF). It can be produced from furfural, a material derived from biomass that has been used as a renewable feedstock in chemical production processes for centuries. Hemicellulose – the part of a plant that binds its structural elements together – is a non-food feedstock forming 20-30% of biomass such as seeds, husks, straws, leaves and wood. Also known as xylan, it is hydrolysed chemically or enzymatically to produce the furfural feedstock for bio MPA.
As one of Earth’s richest polysaccharide sources – alongside starch, glycogen – hemicellulose is attracting increasing attention due to its biodegradability, renewability abundance. While cellulose is an un-branched long chain polymeric molecule comprising the glucose monomers of plant cell walls, hemicelluloses are branched and shorter in length than cellulose.