Global Isostatic Pressing Market Outlook 2031
- The global industry was valued at US$ 8.2 Bn in 2022
- It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2023 to 2031 and reach US$ 15.8 Bn by the end of 2031
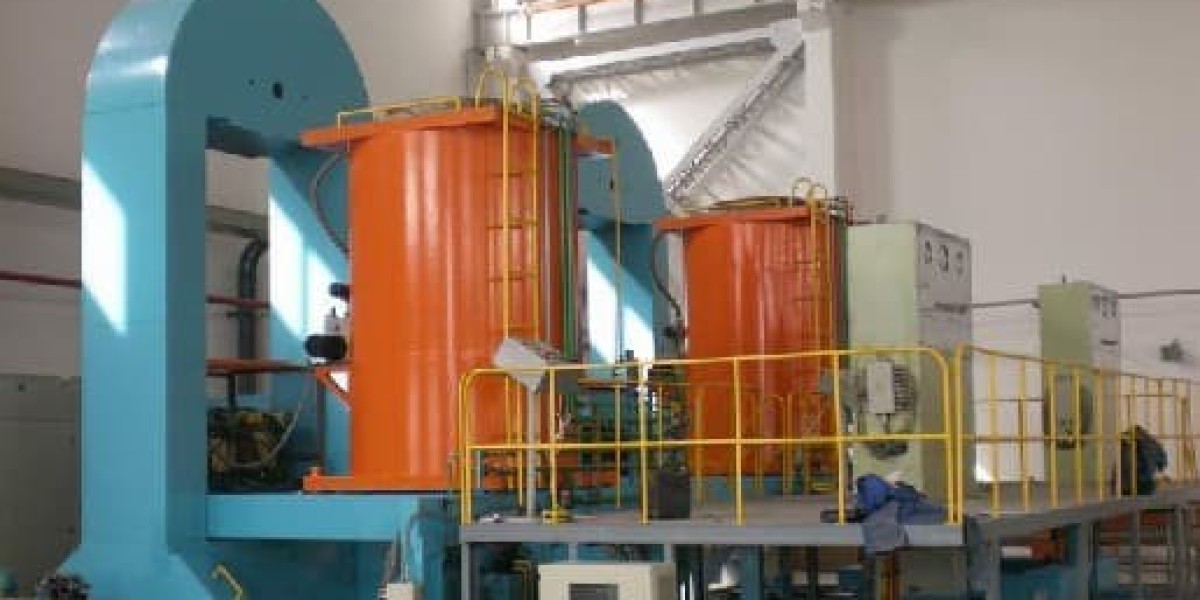
Isostatic pressing is a manufacturing process that applies equal pressure in all directions on a powder compact, thus achieving maximum uniformity of density and microstructure without the geometrical limitations of uniaxial pressing.
For More Information, Click Here: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=S&rep_id=70077
It involves subjecting a material, typically a powder, to high pressure in a sealed container filled with a fluid or gas medium. The pressure is evenly distributed, allowing for uniform compaction and consolidation of the material.
Isostatic pressing is performed cold, warm, or hot. Cold isostatic pressing (CIP) is used on compact green parts at ambient temperatures. Warm isostatic pressing (WIP) is used to shape and press material at a warm temperature. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is used on fully consolidated parts at elevated temperatures by solid-state diffusion.
Technological advancements and ongoing R&D has expanded the range of applications for isostatic pressing, as it is widely used in the production of aerospace and automotive components, medical implants, semiconductor materials, and even 3D printing.