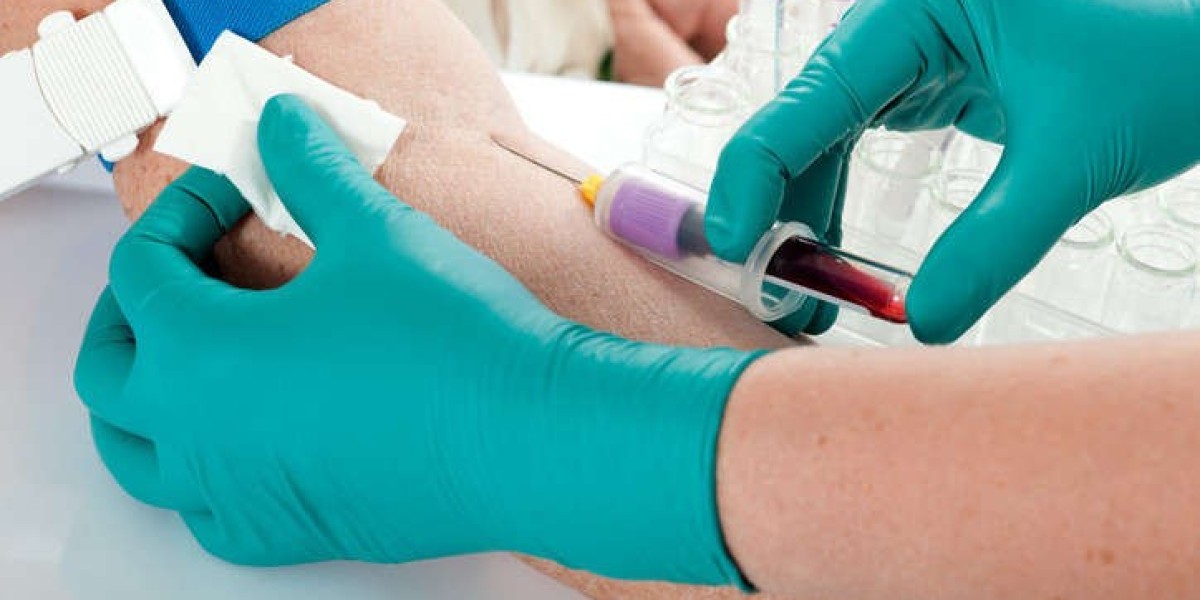
Drawing blood is a crucial part of medical care and diagnostic testing. It allows healthcare providers to assess a patient's health, diagnose medical conditions, and monitor treatment progress. The process involves accessing a vein to collect a blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Proper technique and adherence to safety protocols are essential to ensure reliable and accurate results.
1. Gather the Necessary Supplies
Before starting the blood draw, gather all the necessary supplies. This includes:
Sterile gloves
Alcohol swabs
Vacutainer or blood collection tubes
Needles
Tourniquet
Gauze pads
Adhesive bandages
Sharps container for safe disposal
It is crucial to use sterile equipment to prevent infections and ensure the integrity of the blood sample.
2. Prepare the Patient
Explain the blood drawing procedure to the patient, addressing any concerns or questions they may have. Ensure the patient is comfortable and positioned appropriately. Typically, the patient's arm is extended and supported, with the palm facing upward for easy access to the veins.
3. Locate the Vein
Identify a suitable vein for blood collection. The most commonly used veins are located in the inner forearm or the back of the hand. Veins should be visible, easily palpable, and have a good blood flow. Techniques such as tapping or applying a warm compress can help dilate the veins and make them more prominent.
4. Cleanse the Area
Cleanse the selected site with an alcohol swab or antiseptic solution. Start from the center and work outward in a circular motion to remove any dirt or bacteria. Allow the area to air dry completely before proceeding.
5. Apply Tourniquet
Apply a tourniquet above the selected site to create venous engorgement. The tourniquet should be tight enough to impede venous blood flow but not excessively so as to cut off arterial circulation. Ensure the patient is comfortable and that the tourniquet does not cause pain or discomfort.
6. Insert the Needle
Using a sterile needle, insert it into the vein at a slight angle. Maintain a steady hand to minimize discomfort for the patient. Blood should appear in the collection tube once the needle has successfully entered the vein.
7. Collect the Blood Sample
Collect the required amount of blood using appropriate collection tubes. Different tests may require different types and quantities of blood samples. Ensure the tubes are correctly labeled with patient information and the type of test being conducted. Fill each tube adequately to ensure accurate results.
8. Remove the Needle
Once the blood sample has been collected, carefully remove the needle from the vein. Apply gentle pressure with a sterile gauze pad over the puncture site to facilitate clotting and prevent bleeding. Secure the puncture site with an adhesive bandage.
9. Post-Procedure Care
Provide post-procedure care instructions to the patient, such as keeping the puncture site clean and dry, avoiding strenuous activities, and monitoring for any signs of infection or complications. Dispose of used supplies in a designated sharps container and document the procedure appropriately in the patient's medical record.
10. Conclusion
Drawing blood is a skill that requires proper training, attention to detail, and adherence to safety protocols. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, healthcare professionals can ensure a smooth and successful blood drawing process. Effective communication, patient comfort, and proper handling of supplies contribute to a positive experience and reliable blood sample collection.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q. Can anyone draw blood, or is it limited to healthcare professionals?
A. Drawing blood is a specialized procedure typically performed by trained healthcare professionals, such as nurses, phlebotomists, or doctors. They have the necessary knowledge and skills to ensure a safe and successful blood draw.
Q. Are there any risks or complications associated with drawing blood?
A. While drawing blood is generally safe, there are potential risks, such as infection, bruising, hematoma formation, or fainting. Following proper procedures and using sterile equipment can minimize these risks.
Q. How long does the blood drawing process usually take?
A. The duration of a blood draw can vary depending on factors such as the patient's vein accessibility, the number of tubes needed, and the patient's cooperation. On average, the process takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
Q. Can patients experience pain during a blood draw?
A. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or a pinching sensation during needle insertion. However, the pain is usually brief and tolerable. Healthcare professionals aim to make the procedure as comfortable as possible for the patient.
Q. Are there any special considerations for drawing blood from pediatric patients or individuals with difficult veins?
A. Drawing blood from pediatric patients or individuals with difficult veins may require additional expertise and techniques. Healthcare professionals may use smaller needles, distraction techniques, or request assistance from specialized phlebotomists when necessary.
Maghanap
Mga Sikat na Post
-
 https://www.facebook.com/Botanical-Farms-CBD-Gummies-110152788210409
Sa pamamagitan ng healthyhug
https://www.facebook.com/Botanical-Farms-CBD-Gummies-110152788210409
Sa pamamagitan ng healthyhug -
 How I found a great resource about online gambling
Sa pamamagitan ng Maxi Rory
How I found a great resource about online gambling
Sa pamamagitan ng Maxi Rory -
 Exploring Anal Sex: Understanding, Safety, and Pleasure
Sa pamamagitan ng Hanry Larson
Exploring Anal Sex: Understanding, Safety, and Pleasure
Sa pamamagitan ng Hanry Larson -
 Exploring the World of Cosplay: Types, History, and Creativity
Sa pamamagitan ng Usman Clark
Exploring the World of Cosplay: Types, History, and Creativity
Sa pamamagitan ng Usman Clark -
 Unlock Business Success with Vet1's Top-notch IT Services in Greenville
Sa pamamagitan ng vet1 greenville
Unlock Business Success with Vet1's Top-notch IT Services in Greenville
Sa pamamagitan ng vet1 greenville
Mga kategorya
- Mga Kotse at Sasakyan
- Komedya
- Ekonomiks at Kalakalan
- Edukasyon
- Aliwan
- Mga Pelikula at Animasyon
- Paglalaro
- Kasaysayan at Katotohanan
- Live na Estilo
- Natural
- Balita at Pulitika
- Tao at Bansa
- Mga Alagang Hayop at Hayop
- Mga Lugar at Rehiyon
- Agham at teknolohiya
- Palakasan
- Paglalakbay at Mga Kaganapan
- Iba pa